Adenoidectomy
An Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the adenoids, which are small, soft tissue masses located at the back of the nasal cavity. These glands play a role in the immune system during childhood, but they often shrink and become less important as children grow older.
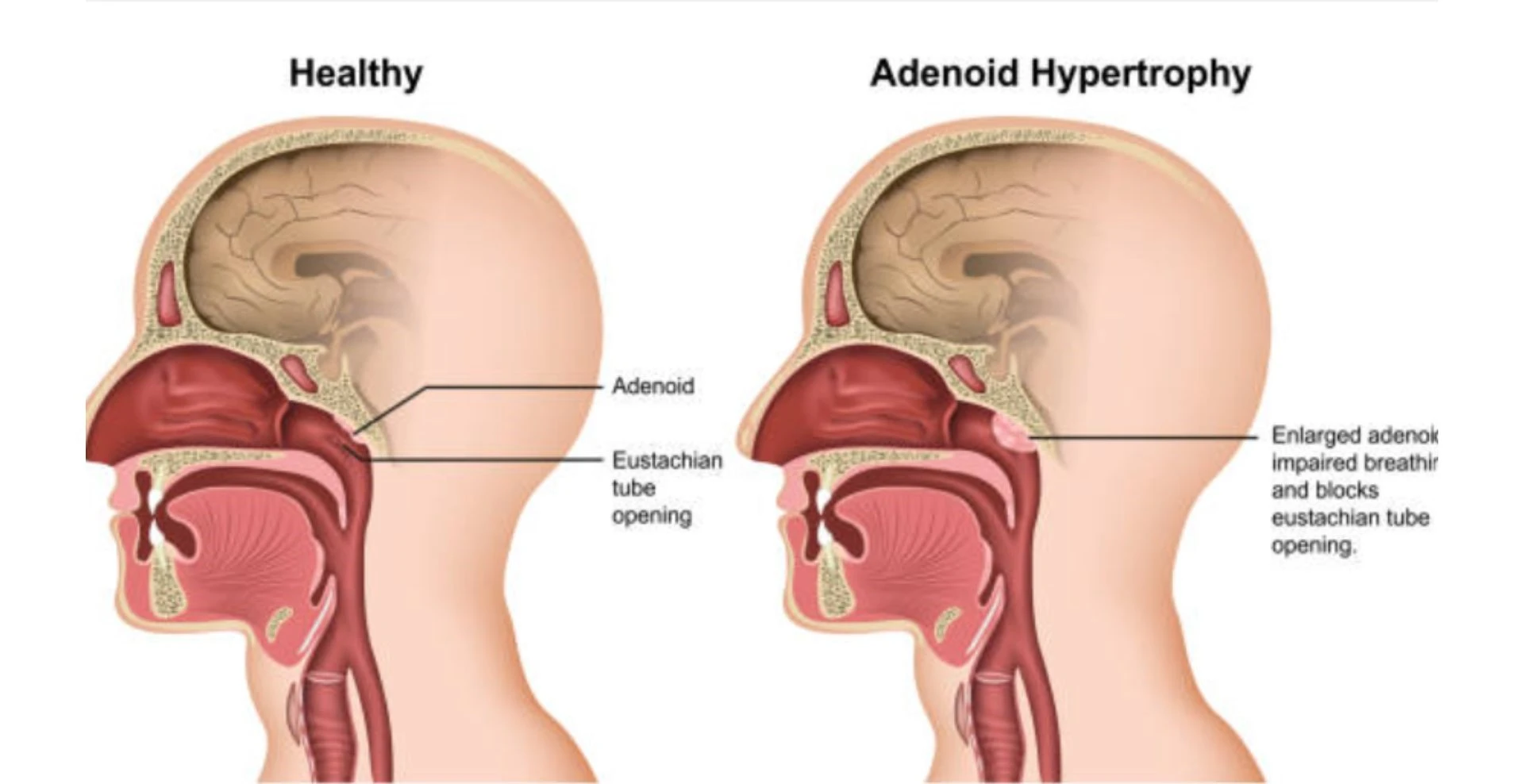
Symptoms that May Indicate a Need for Adenoidectomy
Some of the common symptoms of adenoid enlargement that may call for an adenoidectomy are recurring ear infections, snoring, difficulty breathing through the nose, mouth breathing, and changes in facial development. If obstructive sleep apnea is due to adenoid enlargement, the patient will exhibit interrupted sleep, daytime fatigue, and abnormal behavior.

When is Adenoidectomy Generally Recommended?
Adenoidectomy is indicated for chronic and recurrent adenoiditis, frequent nasal infections, or dyspnea due to adenoid hypertrophy. The other indications are sleep apnoea, chronic ear problems, and very rarely, tumours of the adenoids. Normally, adenoidectomy is usually indicated in cases of refractory or recurrent adenoid infection, nasal obstruction, and breathing problems because of the presence of hypertrophied adenoids. It also can be advised in instances such as sleep apnea, chronic ear issues, and rarely, adenoid tumors.
- Chronic or recurrent adenoiditis
- Frequent nasal infections
- Nasal obstruction or breathing difficulties
- Sleep Apnea
- Chronic ear Infections or Middle Ear Fluid
- Rare cases of adenoid Tumors
The Adenoidectomy Procedure
Adenoidectomy involves surgical removal of the adenoids, which can be performed by traditional surgical techniques, endoscopic, or cautery methods to reduce bleeding and discomfort.
1
Preparation
2

Accessing the Adenoids
3

Removal of the Adenoids
4

Post-Procedure Care
Recovery & Aftercare
- Typical recovery timeline (1–2 weeks)
- Common post-surgery symptoms: Nasal congestion, sore throat, mild fever
- Warning signs to watch for: Excessive bleeding, high fever, breathing issues
- Tips for a smooth recovery: As advised by the Doctor
